Euramerica
An editor has performed a search and found that sufficient sources exist to establish the subject's notability. (October 2024) |
Euramerica (also known as Laurussia – not to be confused with Laurasia, – the Old Red Continent or the Old Red Sandstone Continent) was a minor supercontinent created in the Devonian as the result of a collision between the Laurentian, Baltican, and Avalonian cratons during the Caledonian orogeny, about 410 million years ago. In the Late Carboniferous, tropical rainforests lay over the equator of Euramerica. A major, abrupt change in vegetation occurred when the climate aridified. The forest fragmented and the lycopsids which dominated these wetlands thinned out, being replaced by opportunistic ferns. There was also a great loss of amphibian diversity and simultaneously the drier climate spurred the diversification of reptiles.[1]
Extent
[edit]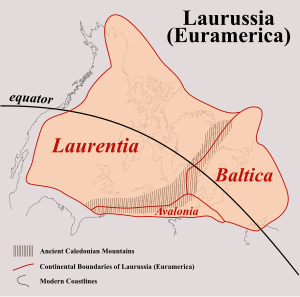
Euramerica became a part of the major supercontinent Pangaea in the Permian. In the Jurassic, when Pangaea rifted into two continents, Gondwana and Laurasia, Euramerica was a part of Laurasia.
In the eocene, Laurasia split into the continents of North America and Eurasia. The Laurentian craton became a part of North America while Baltica became a part of Eurasia, and Avalonia was split between the two.
Events by period
[edit]- Devonian: The first forests grew in the floodplain around the foothills of the Caledonian mountain range.[2]
- Carboniferous: Climate change devastated tropical rainforests, fragmenting the forests into isolated 'islands' and causing the extinction of many plant and animal species during the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse (CRC).
- Permian: Euramerica became a part of the supercontinent Pangaea.
- Jurassic: Pangaea rifted into Gondwana and Laurasia.
- eocene: Laurasia split into the continents of North America, Europe and Asia.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Sahney, Sarda; Benton, Michael J.; Falcon-Lang, Howard J. (2010). "Rainforest collapse triggered Pennsylvanian tetrapod diversification in Euramerica" (PDF). Geology. 38 (12): 1079–1082. doi:10.1130/G31182.1.
- ^ "3. New Frontiers". Miracle Planet. National Board of Film (Canada) and NHK (Japan). 2006. Discovery Channel.











